
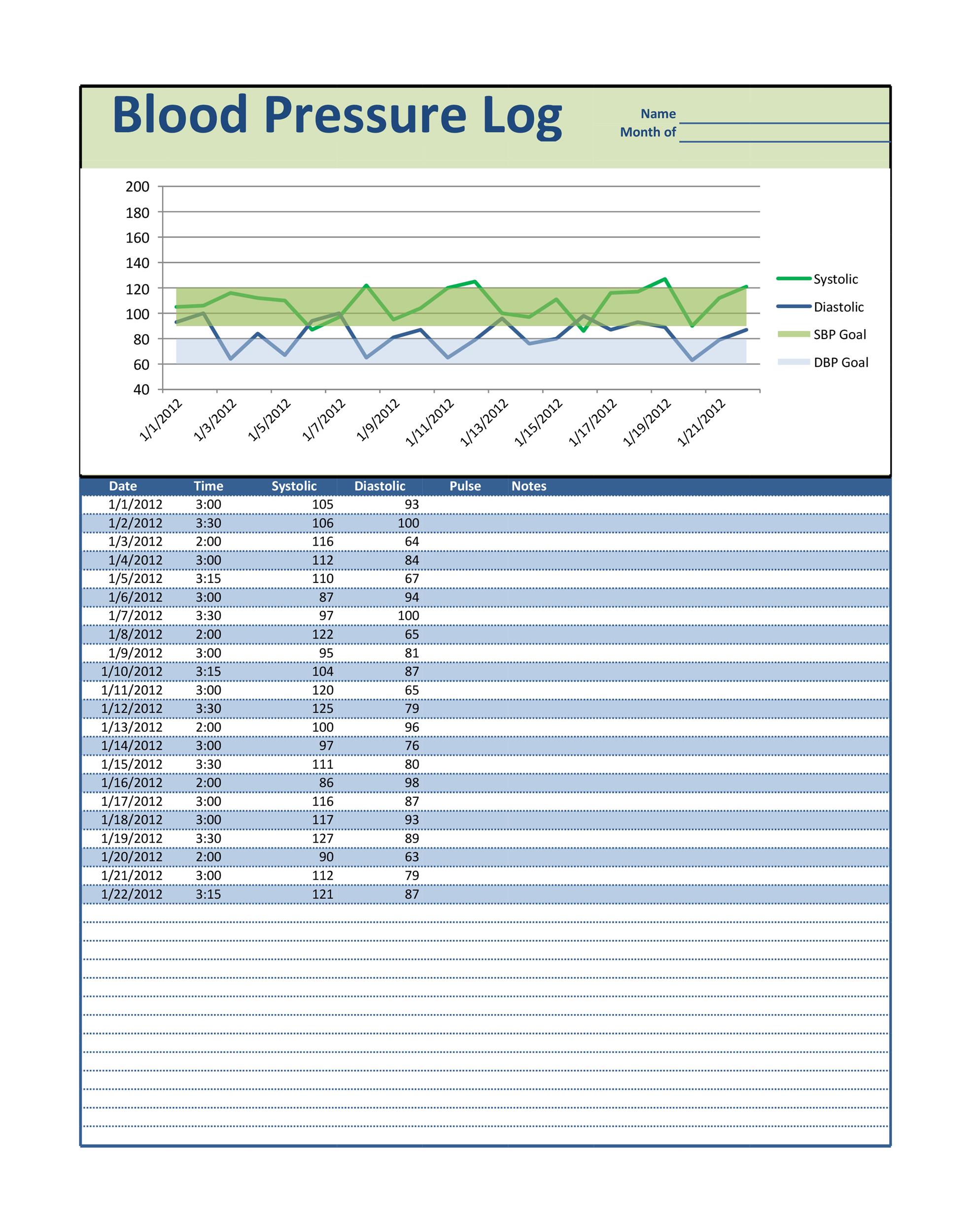
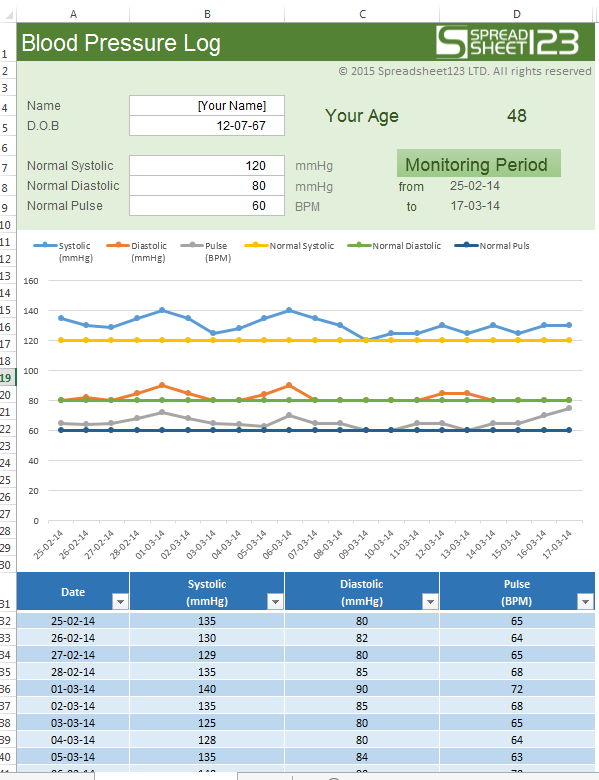
And when you are sick or have to spend some days in hospitals, you will notice that your blood pressure is measured over time and they write it down a piece of paper. If your blood pressure reading is higher than normal, your doctor may take several readings over time and/or have you monitor your blood pressure at home before diagnosing you with high blood pressure. Based on statistic, about one in three (33.5%) U.S. While it can change from everytime with changes in posture, exercise, stress or sleep, it should normally be less than 120/80 mm Hg for an adult age 20 or over. Your blood pressure rises with each heartbeat and falls when your heart relaxes between beats. What is the value of normal blood pressure? Starting at age 20, the American Heart Association recommends a blood pressure screening at your regular healthcare visit or once every 2 years, if your blood pressure is less than 120/80 mm Hg. Systolic (top number), measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats, and Diastolic (bottom number) measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats. It is typically recorded as the ratio of two numbers, the systolic pressure over diastolic pressure, like 120/80 (in mmHg).
It is measured on the inside of an elbow at the brachial artery, which is the upper arm’s major blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart. Usually, doctors or nurses are measuring blood pressure at a person’s upper arm. And also it is influenced by some factors, for example earth gravity, valves in veins, and pumping from contraction of skeletal muscles, which make the value is not the same in various place inside the body.
Blood pressure drops most rapidly along the small arteries and arterioles, and continues to decrease as the blood moves through the capillaries and back to the heart through veins. It decreases as the circulating blood moves away from the heart through arteries.
During each heartbeat, it varies between a maximum (systolic) and a minimum (diastolic) pressure. Blood pressure is usually refers to the arterial pressure of the heart systemic circulation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
